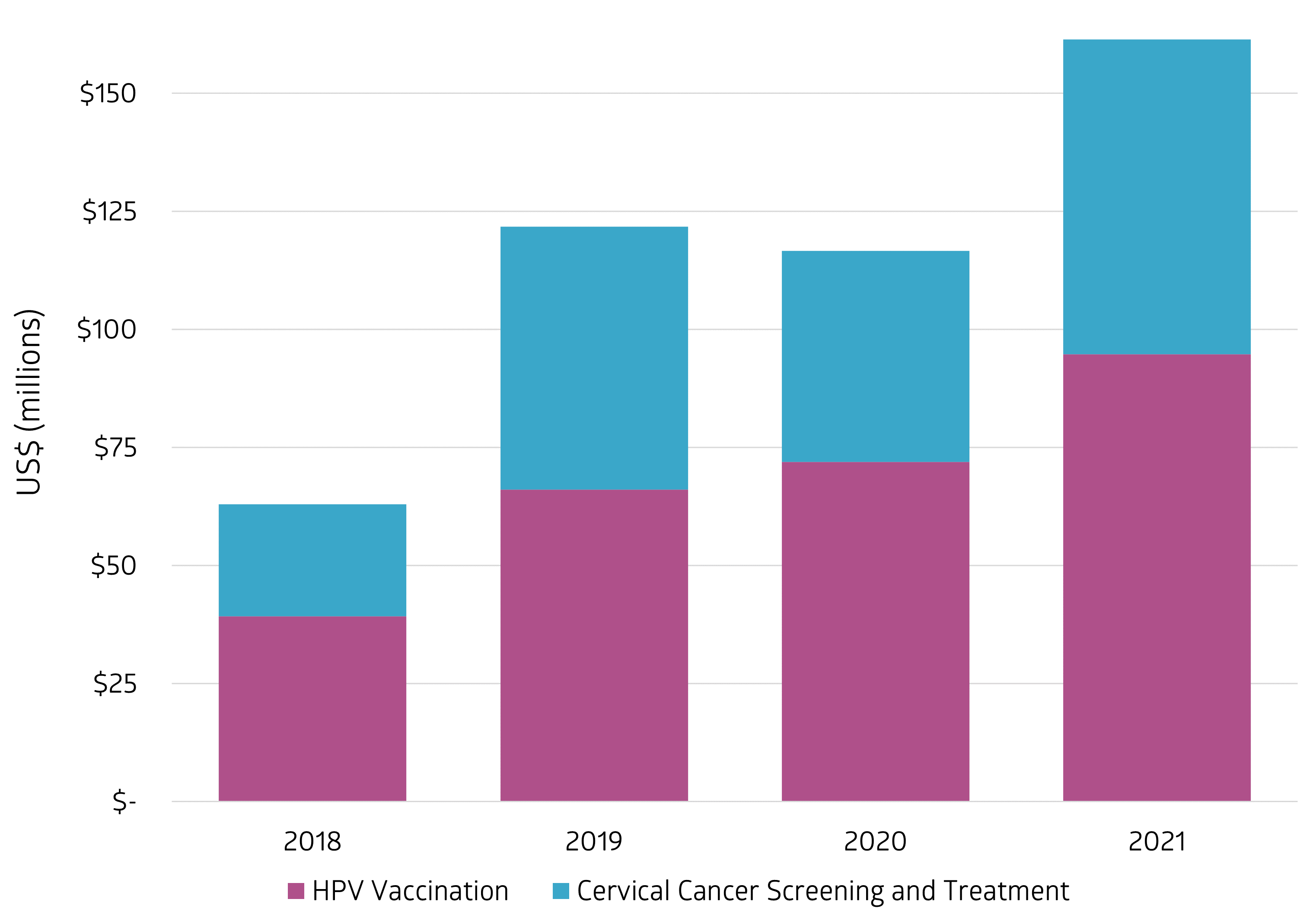Investing in Global Cervical Cancer Prevention: Resources for Low-Income and Lower Middle-Income Countries in 2022
Effective, low-cost interventions to prevent and treat cervical cancer are available today, but far too many women in low-resource settings lack access to these lifesaving tools. Sufficient investment can change this reality and put the world on the path to ending this preventable killer of women around the world.
Resources for cervical cancer prevention, screening, and treatment remain insufficient to change the trajectory of this global epidemic. Better data on current investments in cervical cancer programs in low-income countries (LICs) and lower middle-income countries (LMICs) can inform decision-makers and provide a basis for advocacy for increased financial and political support.
TogetHER for Health publishes an annual analysis of funding for cervical cancer prevention in low-income countries (LICs) and lower middle-income countries (LMICs). Our newest report summarizes investments in HPV immunization and cervical cancer screening and treatment in LICs and LMICs from 2018 through 2022. Read the latest report!
Highlights:
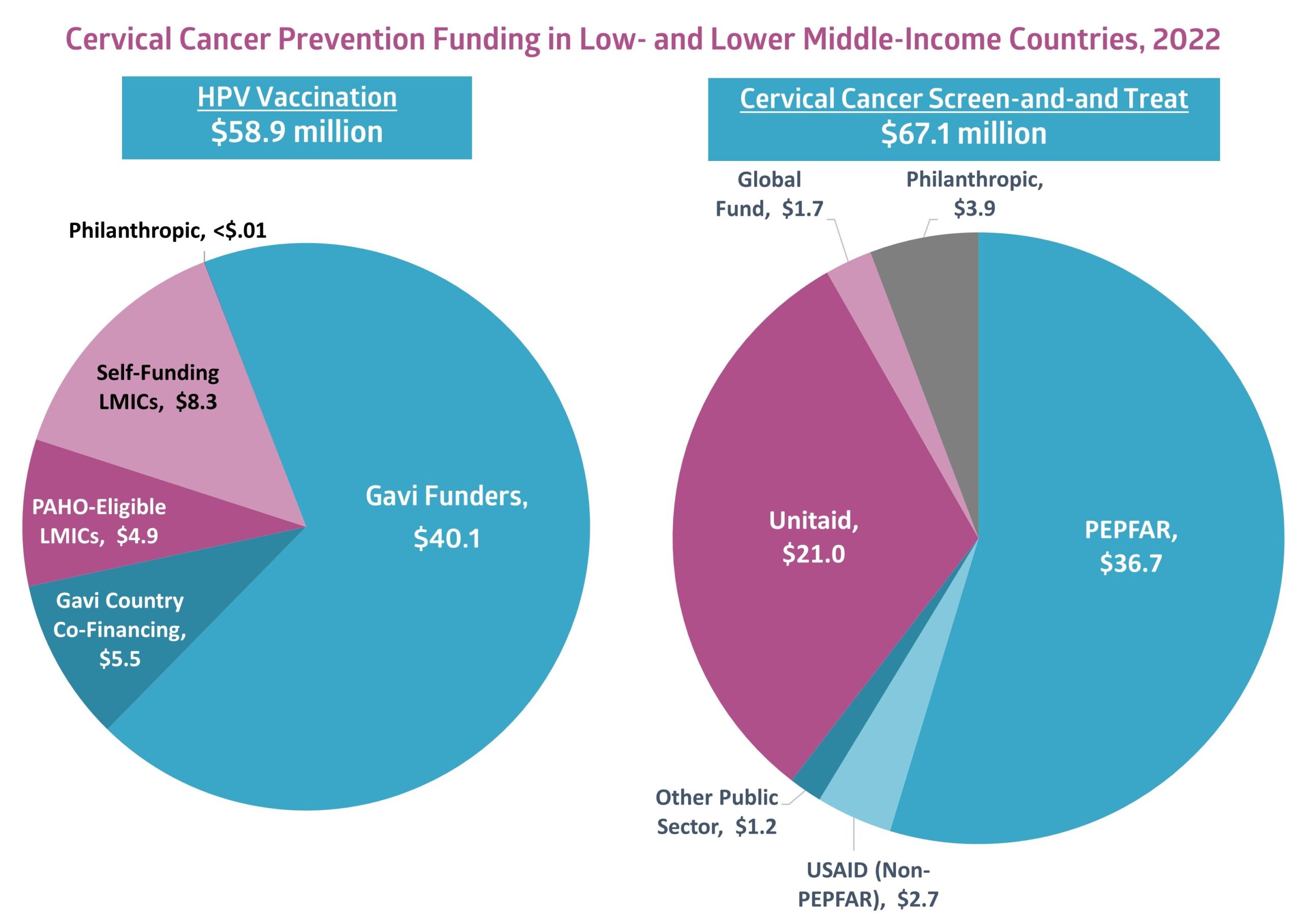
- In 2022, a total of US$58.9 million was invested in HPV vaccine programming in low- and lower middle-income countries, a year-to-year reduction of 44.2% largely attributed to use of vaccine stocks not dispensed during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- US$67.1 million was invested in cervical cancer screen-and-treat programs in 2022, a slight year-to-year increase of 0.7%.
- Estimated five-year funding for HPV vaccination (2018-2022) totaled $345.3 million, an annual average of $69.1 million.
- Estimated five-year funding for cervical cancer screening and treatment (2018-2022) totaled $257.8 million, averaging $51.6 million per year.
- Funding remains grossly insufficient to achieve World Health Organization targets for the scale-up of cervical cancer elimination targets by 2030.